Reading-notes
Arrays, Loops, Imports
Packages and Import :
-packages its the same of “directory”. A package is a single folder (directory) containing a group of related classes (.java files) and interfaces.
- Import statments allowed you to name the packages from other libraries .
Package declaration :
-A package declaration, if used, must be the first thing in the file, and describes the folder in which it occurs.
Package declaration syntax:
- The statement order is as follows. Comments can go anywhere.
- Package statment (optional).
- Imports (optional).
- Class or interface definitions.
Imports: three options:
if we take an example to see what the three options , we have JOptionPane class , this class located in the swing package which is located in the javax package.
The wildcard character (*) is used to specify that all classes with that package are available to your program:
- import javax.swing.*; // Make all classes visible altho only one is used.
Classes can be specified explicitly on import instead of using the wildcard character: -import javax.swing.JOptionPane; // Make a single class visible.
Alternately we can the fully qualified class name without an import like in this ex :
- class ImportTest { public static void main(String[] args) { javax.swing.JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(null, “Hi”); System.exit(0); }}
Common imports :
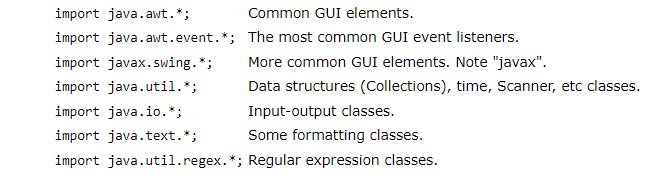
Java 5 added an import static option that allows static variables (typically constants) to be referenced without qualifying them with a class name.
A Guide to Java Loops :
- Types of loops that we can find in Java:
- Simple for loop
- Enhanced for-each loop
- While loop
- Do-While loop
for-loop :
- an entry-controlled loop that facilitates a user to execute a block of a statement(s) iteratively for a fixed number of times.
while loop :
- a control flow statement that allows code to be executed repeatedly based on a given Boolean condition.
Do-While Loop :
- is used to iterate a part of the program repeatedly, until the specified condition is true.