Reading-notes
WRRC and Java
The HTTP Request Lifecycle:
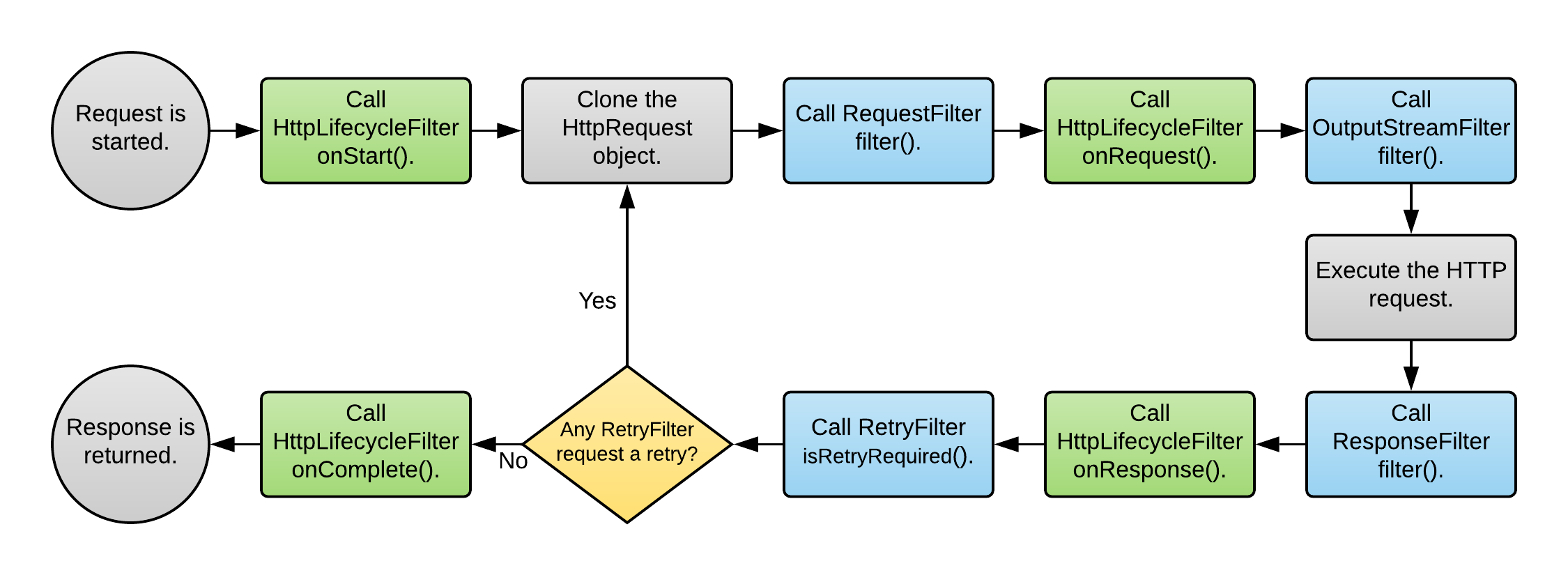
-
HTTP 1.1 request,
not a persistent connection, but it could act as a good jumping-off point for HTTP/2 and persistent connection requests.
some various HTTP methods:
-
Local Processing : depending on the application making the request.
-
Resolve an IP:
adding entries in the local hosts file on a computer.
-
Establish a TCP Connection:uses a three-way handshake:
- SYN: The active open is performed by the client sending a SYN to the server.
- SYN-ACK: In response, the server replies with a SYN-ACK.
- ACK: Finally, the client sends an ACK back to the server.
-
Send an HTTP Request:
An HTTP client sends an HTTP request to a server in the form of a request message which includes following format:
- A Request-line.
-
Zero or more header (General Request Entity) fields followed by CRLF. -
An empty line.
-
Tearing Down and Cleaning Up :
At this point, your browser begins processing what it has received. If it is an image, data, or other media file that is being consumed by some application inside the browser, a variety of things can happen.
- Well, that is it, that is the multi-layer lifecycle of a single HTTP request!
steps for example:
-
a way of performing HTTP requests in Java:
by using the built-in Java class HttpUrlConnection.
-
HttpUrlConnection:
The HttpUrlConnection class allows us to perform basic HTTP requests without the use of any additional libraries. All the classes that we need are part of the java.net package.
-
Creating a Request:
We can create an HttpUrlConnection instance using the openConnection() method of the URL class.
-
Adding Request Parameters:
we have to set the doOutput property to true, then write a String of the form param1=value¶m2=value to the OutputStream of the HttpUrlConnection instanc
-
Setting Request Headers:
Adding headers to a request can be achieved by using the setRequestProperty() method.
-
Configuring Timeouts:
HttpUrlConnection class allows setting the connect and read timeouts.
-
Handling Cookies:
The java.net package contains classes that ease working with cookies such as CookieManager and HttpCookie.
-
Handling Redirects:
We can enable or disable automatically following redirects for a specific connection by using the setInstanceFollowRedirects() method with true or false parameter.
-
Reading the Response:
by parsing the InputStream of the HttpUrlConnection instance. To execute the request, we can use the getResponseCode(), connect(), getInputStream() or getOutputStream() methods.
-
Reading the Response on Failed Requests
If the request fails, trying to read the InputStream of the HttpUrlConnection instance won’t work. Instead, we can consume the stream provided by HttpUrlConnection.getErrorStream().
-
11. Building the Full Response :
It’s not possible to get the full response representation using the HttpUrlConnection instance. we can build it using some of the methods that the HttpUrlConnection instance offers.